Mussel vs Clams: A Comprehensive Comparison
When it comes to seafood, mussels and clams are two popular choices that grace many menus and dinner tables. Both belong to the bivalve family and share similarities in appearance, taste, and texture. However, there are also key differences that set them apart. In this article, we will delve into the world of mussels and clams, comparing them in terms of habitat, anatomy, taste, nutritional value, and cooking methods.

Mussels vs Clams
I. Habitat:
Mussels:
- Mussels are primarily found in both freshwater and saltwater environments.
- They often attach themselves to rocks, piers, or other surfaces using strong byssal threads.
- Common types of mussels include the Blue mussel, Green-lipped mussel, and Mediterranean mussel.
Clams:
- Clams are predominantly found in sandy or muddy bottoms of saltwater habitats.
- They have the ability to burrow into the substrate to protect themselves.
- Well-known varieties of clams include Hardshell clam, Softshell clam, and Quahog clam.
II. Anatomy:
Mussels:
- Mussels have elongated shells that are generally dark or bluish-black in color.
- They possess a muscular "foot" that helps them move and attach to surfaces.
- The inner flesh of mussels is soft and orange or pale in color.
Clams:
- Clams have rounded shells that can vary in color, ranging from light to dark brown.
- They feature a siphon, which enables them to draw in water and filter out food particles.
- The inner flesh of clams is firmer and can range from white to light brown.
III. Taste and Texture:
Mussels:
- Mussels have a distinct flavor that is often described as sweet and slightly briny.
- They offer a tender and meaty texture that can be slightly chewy when cooked.
Clams:
- Clams have a mild and slightly salty taste, often compared to the flavor of the ocean.
- They have a more delicate and tender texture compared to mussels.
Mussels vs Clams
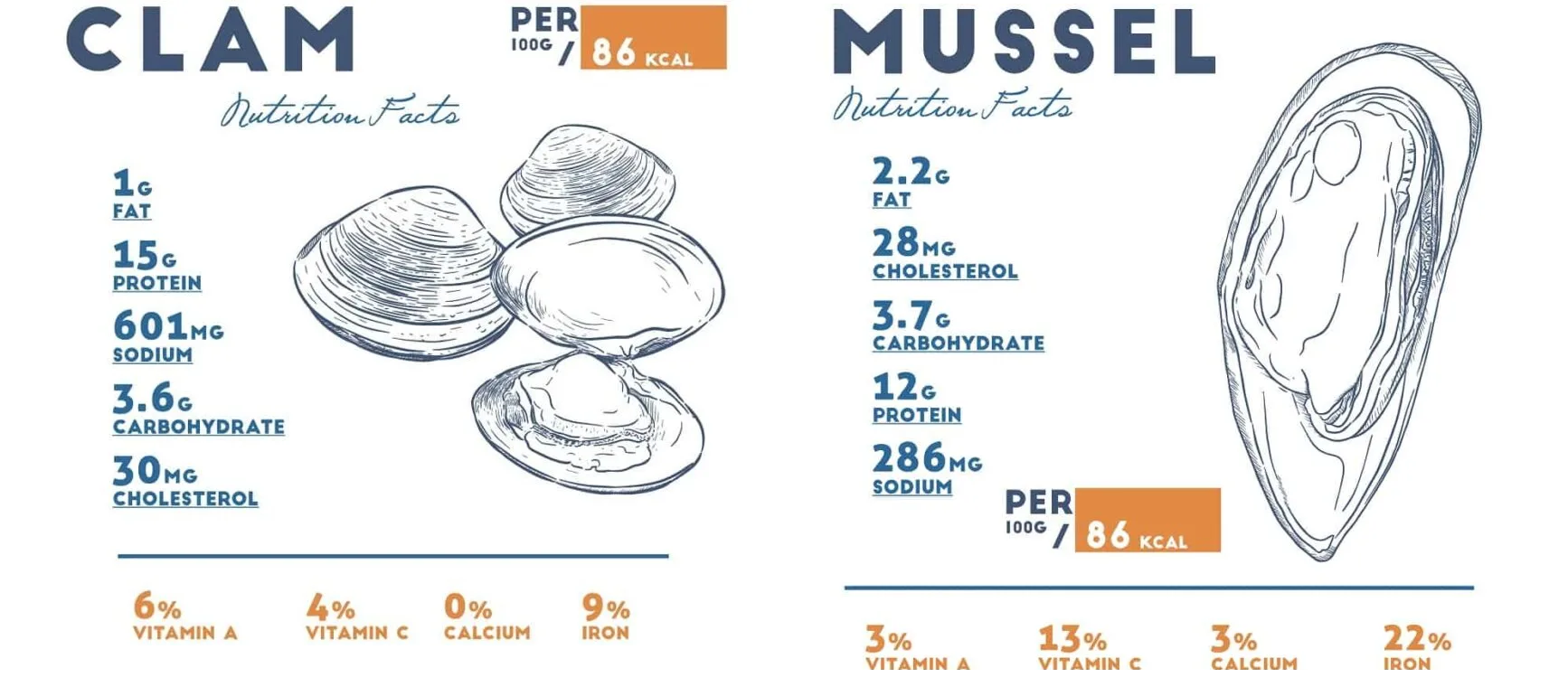
IV. Nutritional Value:
Mussels:
- Mussels are highly nutritious, packed with essential vitamins and minerals.
- They are an excellent source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, iron, and vitamin B12.
- Mussels also provide a good amount of selenium and iodine.
Clams:
- Clams are similarly rich in nutrients, including protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and iron.
- They are also a good source of vitamins A and C, as well as potassium.
- Clams contain lower levels of fat and calories compared to mussels.
V. Cooking Methods:
Mussels:
- Mussels are commonly steamed, boiled, or used in stews and soups.
- They are often paired with white wine, garlic, and herbs for a classic preparation.
- Mussels can also be grilled or baked for a different flavor profile.
Clams:
- Clams are often steamed, baked, or used in pasta dishes and chowders.
- They are frequently prepared with butter, garlic, and lemon for a simple yet delicious taste.
- Clams can also be enjoyed raw as part of seafood platters or in sushi.
In the battle of mussels vs clams, both offer unique characteristics that make them appealing to seafood enthusiasts. Whether you prefer the slightly chewy texture and briny sweetness of mussels or the delicate taste and tender texture of clams, these bivalve mollusks provide a delicious and nutritious addition to any meal. So, the next time you're at a seafood restaurant or planning a seafood feast, consider trying both mussels and clams to truly appreciate the flavors and textures they have to offer.