North vs. South Vietnam: A Comprehensive Comparison
North and South Vietnam were two distinct regions that emerged as a result of the Vietnam War. This historical conflict divided the nation along ideological lines, leading to profound differences between the two regions. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of the north-south divide in Vietnam and explore various aspects that set them apart. By understanding the political, cultural, economic, and social disparities between North and South Vietnam, we can gain valuable insights into the legacy of the Vietnam War and its impact on the nation.
1. Historical Background
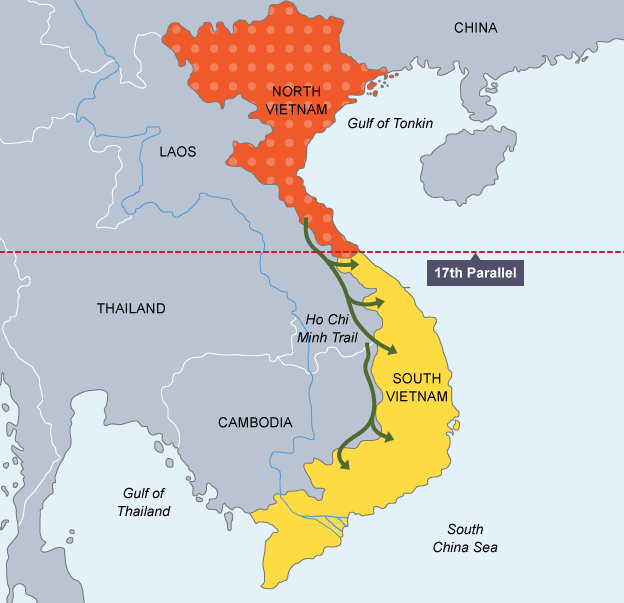
To comprehend the differences between North and South Vietnam, it is crucial to delve into their historical contexts. Following the Geneva Accords of 1954, Vietnam was partitioned into two zones: the communist-led Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North Vietnam) and the U.S.-supported Republic of Vietnam (South Vietnam).
The contrasting political systems and ideological beliefs formed the basis of the north-south divide, ultimately culminating in the Vietnam War.
north vs south vietnam
2. Political Differences
The political divide between North and South Vietnam was perhaps the most significant aspect of their dissimilarity. North Vietnam adhered to a communist regime under the leadership of Ho Chi Minh, while South Vietnam adopted a non-communist government. T
his disparity resulted in contrasting governance structures, policies, and alliances. The North followed a centrally planned economy and pursued close ties with the Soviet Union and China, while the South adopted a market-oriented approach and relied on the support of the United States and its allies.
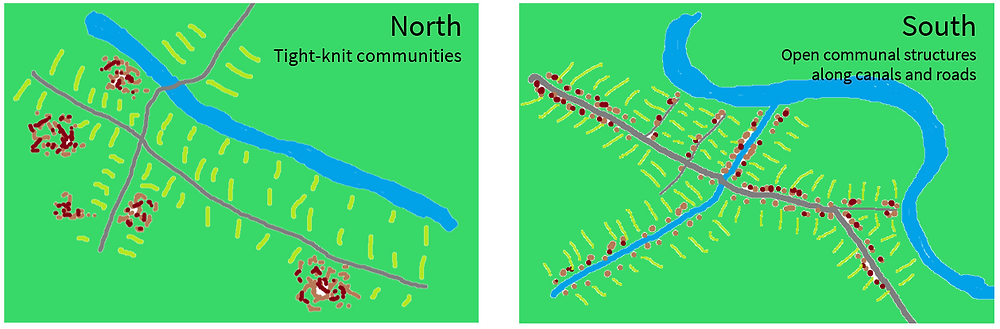
3. Cultural and Social Contrasts
North and South Vietnam exhibited notable cultural and social distinctions due to the divergent historical influences and experiences of their populations. The North placed greater emphasis on collectivist values and traditions, prioritizing communal welfare over individual interests.
Conversely, the South experienced a blend of Western and Vietnamese cultural influences, resulting from the presence of foreign powers throughout history.
This led to a more individualistic and urbanized society in the South, marked by greater exposure to Western ideals and consumerism.
north vs south vietnam
4. Economic Disparities
Economically, North and South Vietnam took contrasting paths due to their respective political ideologies. The North implemented a planned economy, emphasizing heavy industry and agriculture, while the South embraced capitalism and free-market principles, focusing on light industry, trade, and services.
The North received substantial aid from communist allies, while the South attracted foreign investment, particularly from the United States.
These disparities led to different levels of development and economic stability between the two regions.
5. Conclusion
The north-south division in Vietnam, stemming from the Vietnam War, left an indelible mark on the nation. The political, cultural, economic, and social disparities between North and South Vietnam had profound implications for the development and reunification of the country.
By analyzing and understanding these differences, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges faced by Vietnam during and after the war.
Today, although the country has reunited, the legacy of the north-south divide continues to influence various aspects of Vietnamese society.
Recognizing and appreciating these differences can foster a greater sense of unity and reconciliation, ultimately contributing to the nation's progress and future growth.